Npm malware today continues to evolve, with attackers publishing malicious code, malicious npm packages, and pypi malicious packages designed to target development workflows, CI/CD pipelines, and open-source ecosystems. The Malicious Code Digest is Xygeni’s ongoing research report that tracks and verifies real malicious packages across npm and PyPI, including confirmed backdoors, data-stealers, credential exfiltration payloads, and automated multi-version malware campaigns.
Our research team updates this page regularly with validated findings, indicators of compromise (IOCs), behavioral patterns, and technical analysis. As a result, developers, AppSec teams, and security engineers can stay ahead of npm malware today and emerging malicious package activity impacting modern software supply chains.
NPM Malware Today: Weekly Summary 20–27 Feb 2026
Researchers confirmed 34 malicious packages, all published in the npm ecosystem during this period.
This week included two higher-impact investigations:
- An npm-based infostealer campaign involving credential theft and session hijacking.
- A malicious Baileys fork targeting the WhatsApp library supply chain.
Observed characteristics (dataset-based)
- 100% npm distribution
- Repeated multi-version publishing (
conduit-utils,launch-darkly-js) - High or atypical version numbers (99.x, 199.99.x)
- Internal- or SDK-style naming patterns
No definitive campaign linkage can be established from naming alone.
Monthly Malware Report: Confirmed Malicious npm Packages in January 2026
Welcome to the latest edition of the Xygeni Malicious Code Digest (Monthly Edition). In February 2026, our research team confirmed more than 230 malicious packages, primarily across npm, with isolated PyPI cases.
February was not only about volume. Alongside automation-driven publishing waves and aggressive version inflation campaigns, we conducted two high-impact investigations:
- A newly uncovered npm-based infostealer campaign capable of credential theft and session hijacking in developer environments.
- A malicious fork targeting the Baileys WhatsApp library supply chain, abusing trust in a popular ecosystem component to infiltrate dependency trees.
These were not simple typosquatting incidents. Both cases involved credential abuse and supply chain manipulation techniques capable of impacting real CI/CD pipelines.
Across the broader dataset, we continued to observe scripted multi-version publishing, inflated versioning schemes, internal-tool impersonation, and classic tactics such as dependency confusion and data exfiltration.
This report is part of our ongoing Malicious Code Digest, where we validate new threats and provide actionable intelligence to help DevSecOps teams stay ahead of supply chain risk.
| Ecosystem | Package | Date |
|---|---|---|
| npm | uxproject11:1.0.0 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | opencraw:2026.2.15 | Feb 20, 2026 |
| npm | react-dropzone-truffle:100.21.9 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | drikssy-sdk-test:1.0.8 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | @powpegtest/powpeg:10.2.0 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | eslint-validator:1.0.2 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | selfbot-lofy:1.2.5 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | ng-vzbootstrap:1.0.1 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | ng-vzbootstrap:1.0.2 | Feb 23, 2026 |
| npm | vds-monarch:1.0.4 | Feb 23, 2026 |
How We Detect Malicious Code in npm Malware and PyPI Malware
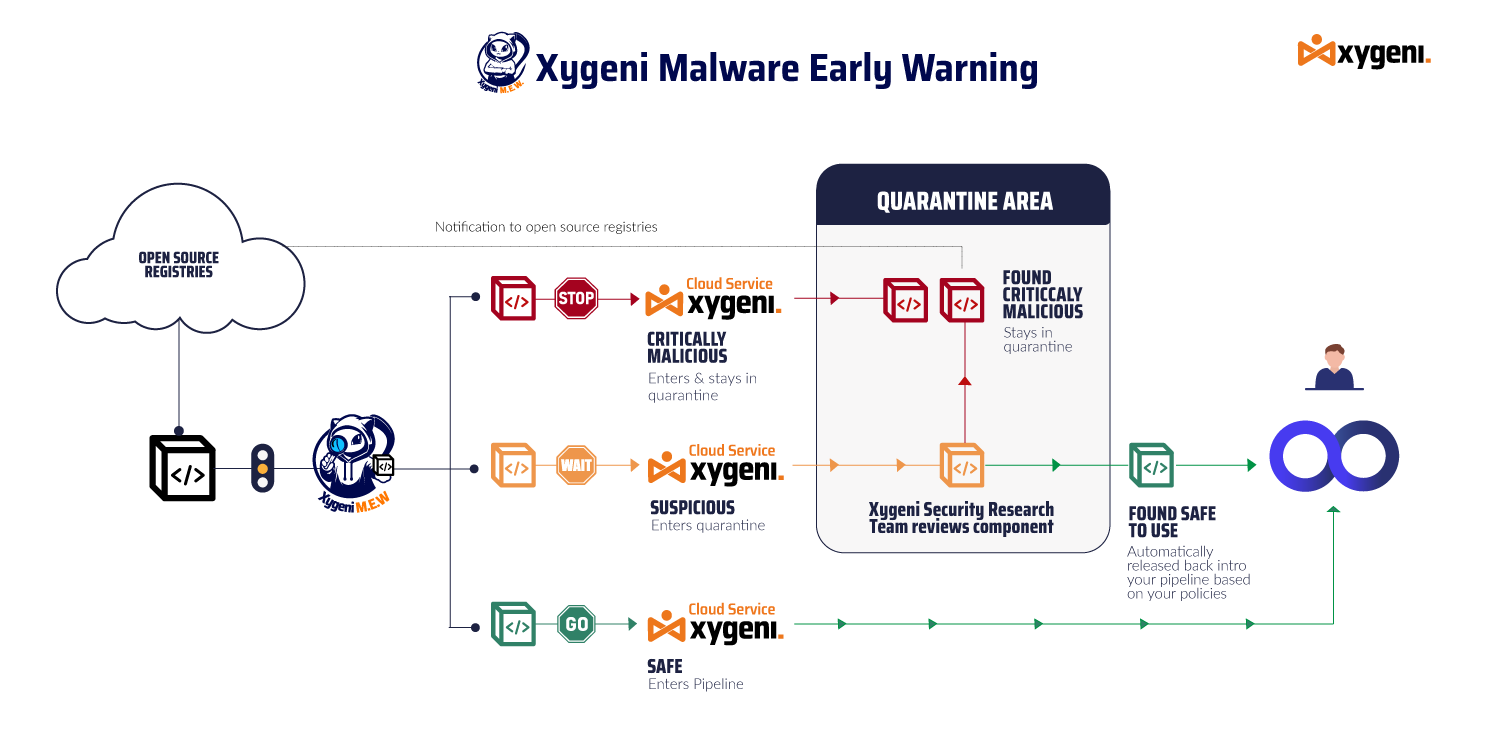
Xygeni uses multi-layered techniques to stop malicious code before it spreads. First of all, static code analysis detects obfuscation patterns, hidden payloads, and script abuse. In addition, behavioral sandboxing analyzes install hooks, runtime commands, and persistence tricks. Moreover, machine learning detection identifies zero-day npm malware and pypi malware variants missed by signature scanners. Finally, the Early Warning System monitors public repositories in real time, validates findings, and alerts DevOps teams immediately.
As a result, this combination ensures developers receive fast, actionable intelligence integrated directly into CI/CD workflows.
Why Developers Should Care About Malicious npm Packages
Modern threats rarely wait for runtime. For example, malicious npm packages often execute during installation, while pypi malicious packages hide token exfiltration or backdoors. Attackers:
- Flip private GitHub repos to public to replicate them.
- Exfiltrate credentials and secrets using encoded payloads.
- Use obfuscated JavaScript loaders to deploy ransomware or botnets.
In fact, malicious open-source packages surged 156% in one year. Therefore, teams that rely only on delayed feeds or basic scanners fall behind.
What This Malware Report Tracks in npm and PyPI
This digest is the central hub for:
- Confirmed malicious npm packages
- Confirmed pypi malicious packages
- Behavior-based detections of malicious code
- Registry-confirmed incidents
- Weekly and monthly malware report summaries
- Historical changelog of all npm malware and pypi malware findings
In other words, it provides a single point of reference. The research team at Xygeni updates this page weekly with links to full technical analyses and GitHub IOCs.
How to Protect Against Malicious npm Packages and PyPI Malware
Because of this growing risk, organizations need more than basic dependency checks. Strong defenses against malicious npm packages and pypi malicious packages require both preventive controls and runtime enforcement:
Enforce Lockfile-Only Installs Against Malicious npm Packages
Use npm ci or pip install --require-hashes in CI/CD.
This ensures the exact dependency tree defined in lockfiles is used. As a result, attackers cannot slip in modified or typosquatted versions of malicious npm packages.
Pre-Install Scanning for npm Malware and PyPI Malware
Integrate Xygeni’s Early Warning Engine to scan npm malware and pypi malware before packages reach your environment.
Moreover, detect suspicious postinstall scripts, obfuscated loaders, or hardcoded C2 URLs.
Guardrails to Block Builds with Malicious Code
Set guardrails to fail builds automatically if confirmed malicious npm packages or pypi malicious packages are detected.
For example, break builds on packages with unpublished maintainers, obfuscation patterns, or IOC matches. Consequently, malicious code never passes unnoticed.
Generate and Validate SBOMs Against Malicious npm Packages and PyPI Malware
Create SBOMs (CycloneDX, SPDX) for every build.
Afterward, compare against known malicious npm packages and pypi malware feeds to track both direct and transitive dependencies.
Credential and Token Protection from npm Malware and PyPI Malware
Many malicious npm packages try to read .npmrc, .pypirc, or environment variables.
Therefore, run builds in hardened containers with minimal secrets exposed. Additionally, use secrets managers instead of environment variables to block malicious code abuse.
Monitor Registry and Maintainer Changes in Malicious npm Packages
Attackers often hijack abandoned projects.
In particular, watch for sudden maintainer swaps, unusual versioning jumps, or excessive publishes in npm malware and pypi malicious packages.
Developer Training on Detecting Malicious Code in npm and PyPI
Teach teams to spot red flags such as:
- Package names with typos (
reqeustinstead ofrequest). - Unusual
installorpreparescripts. - Recently created packages with suspiciously high version numbers.
Above all, this awareness helps detect malicious code early.
Runtime Anomaly Detection for Malicious npm Packages and PyPI Malware
Even if malware bypasses static checks, runtime detection in CI/CD can catch:
- Unexpected network connections.
- File system modifications outside expected directories.
- Persistence attempts across jobs.
Finally, this ensures npm malware and pypi malware threats are stopped even after installation.
By combining these controls, teams prevent malicious npm packages and pypi malicious packages from ever reaching production pipelines.
Try Xygeni’s Malware Detection Tools
Xygeni delivers:
- Real-time detection of malicious code, including backdoors, spyware, and ransomware.
- In contrast to basic scanners, analysis across npm, PyPI, Maven, NuGet, RubyGems, and more.
- Automatic build blocking when the malware report identifies risk.
- Exploitability insights, maintainer reputation checks, and anomaly detection.
Stay Informed
Our team updates this page every week. To receive alerts and detailed reports:
- Subscribe to our Newsletter
- Follow @XygeniSecurity on Linkedin
- Bookmark this page to track the latest npm malware and pypi malware threats