Did you know that over 560,000 new malware threats emerge every single day? As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated, understanding what is malicious code and how it can infiltrate systems is crucial, as these threats can exploit software vulnerabilities, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and major disruptions. Various types of malicious code, such as phishing schemes, trojans, and supply chain exploits, have demonstrated their damaging potential.
For example, the 2023 Ledger attack compromised the company’s software connect-kit tool, allowing attackers to steal over $600,000 by targeting hardware wallets.
What is Malicious Code and Why It Matters
What is malicious code?
Malicious code is software or scripts designed to harm systems or steal data. Unlike legitimate software, it often hides in trusted applications, making it difficult to detect. Examples include viruses, ransomware, and spyware. Advanced detection tools are essential for identifying and preventing it.
Malicious code attacks can exploit both proprietary and open-source software, putting sensitive information at risk. Common types of malicious code include viruses, worms, ransomware, trojans, and spyware. These threats often enter systems through phishing emails, fake software updates, or compromised code from supply chain attacks.
Detection tools, like Xygeni’s Early Warning Malware Detection, are pivotal in identifying and blocking these threats before they compromise systems.
Types of Malicious Code That Can Compromise Your Systems
Now that we’ve defined malicious code, let’s explore the different types that threaten your systems every day.
Types of Malicious Code
- Backdoor: Lets attackers skip authentication to access systems, steal data, or take control.
- Trojan Horses: Software that looks safe but hides harmful code to attack your system.
- Ransomware: Locks your files and demands money to unlock them, disrupting operations.
- Spyware: Secretly watches your activity and steals private information like passwords.
- Phishing Attacks: Fake emails trick you into sharing personal details or downloading harmful files.
- Keyloggers: Records what you type to steal passwords and sensitive information.
- Stealer: Steals stored data, including passwords and important files.
- Worm: Spreads across networks, slowing down systems and using up resources.
- Miner: Uses your computer’s power to mine cryptocurrency, causing poor performance.
How to Defend Against Malicious Code
Open-source software (OSS) encourages collaboration and innovation, but it also creates opportunities for attackers to inject malicious code. Once inside, this code can spread through supply chain attacks, stealing data, controlling systems, or compromising entire networks.
For example, attackers might add malware to a popular open-source library. A notable case is the Polyfill.io attack, where a malicious actor gained control of the Polyfill service and injected malware into its codebase. This compromised over 100,000 websites globally, redirecting mobile users to fraudulent websites. When developers unknowingly integrated the compromised library, they exposed their applications and users to serious risks.
To combat these threats, organizations must implement continuous monitoring, conduct code audits, and use advanced malware detection tools. Developers and users alike must stay vigilant to protect their systems from hidden threats.
Proven Strategies to Defend Against Malicious Code
Malicious code attacks not only compromise systems but can also lead to significant financial losses. Cyberattacks cost businesses an average of $4.45 million per breach, according to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report. This highlights the importance of proactive defenses to avoid the high costs of inaction. To effectively protect your systems, organizations should adopt these strategies:
- Secure Coding Practices: Use static analysis tools to identify vulnerabilities during development.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct regular penetration tests to uncover weaknesses.
- Patch Management: Automate updates to ensure timely application of software patches.
- Application Whitelisting: Restrict execution to pre-approved applications, blocking unauthorized programs.
- Integrate Security in the SDLC: Embed security measures throughout the Software Development Life Cycle.
- Code Review and Binary Analysis: Regularly review code and binaries to detect suspicious behaviors or malicious scripts.
Stay One Step Ahead: Xygeni’s Early Warning Malware Detection
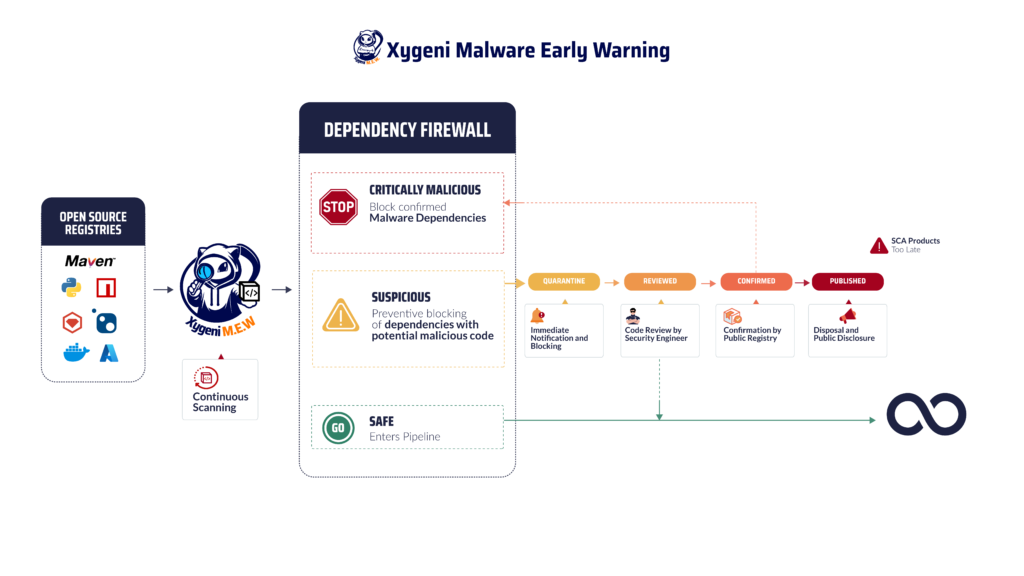
Malicious code is a growing threat, particularly in open-source ecosystems. Xygeni’s Early Warning Malware Detection Tool offers a state-of-the-art solution to combat these risks. This tool not only scans open-source packages for threats but also provides proactive measures to ensure malicious scripts never compromise your software development lifecycle.
How the Early Warning Malware Detection Tool Protects Your Organization
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Xygeni continuously monitors public registries for any signs of malware. This includes scanning for suspicious patterns or malicious behaviors in new and existing open-source packages. By acting in real-time, Xygeni identifies and isolates threats before they infiltrate your CI/CD pipeline.
- Automatic Quarantine: When malicious code is detected, Xygeni automatically quarantines the threat, ensuring it cannot affect your systems or propagate through the supply chain. This process includes the integration of security guardrails to block risky packages, reducing remediation work later.
- Comprehensive Vulnerability Management: Beyond known vulnerabilities, Xygeni’s tool addresses zero-day threats, sophisticated polymorphic malware, and unregistered vulnerabilities. This proactive stance is vital in dealing with the evolving tactics of attackers.
- Detailed Notifications: When a threat is identified, the tool immediately notifies your team through email, messaging platforms, or webhooks. This ensures rapid response and minimal downtime for your projects.
- Regulatory Compliance and Reporting: Xygeni aligns with standards like NIS2 and DORA, ensuring that your software development practices remain compliant. Features like Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) generation provide transparency and support operational resilience.
Safeguarding Against the Types of Malicious Code
Xygeni’s tool is designed to defend against a variety of malware types, including:
- Backdoors and Trojans: Detects unauthorized access points and disguised threats that compromise systems.
- Ransomware: Blocks code that encrypts your files or demands ransom payments.
- Spyware and Keyloggers: Prevents the collection of sensitive user data or system keystrokes.
- Cryptocurrency Miners: Identifies and stops resource-draining code used for unauthorized crypto mining.
By integrating these capabilities, the Early Warning Malware Detection Tool ensures your software remains resilient against emerging threats.
Do you want to go deeper?
If you’re still thinking about what it is or want to better understand the types of malicious code threatening your CI/CD pipeline and how to prevent them, check out our blog post on protection and learn how to spot hidden risks early.
Cyber threats evolve daily, shouldn’t your defenses evolve too? Understanding what is malicious code and recognizing the various types of malicious code targeting your infrastructure is only the starting point. True security comes from proactive defense. By equipping your organization with advanced malware detection tools, you can identify and block hidden threats before they infiltrate your systems. Reactive security isn’t enough, staying one step ahead is the only real strategy.
Don’t Wait for an Attack: Protect Your Systems Now!
The rise of malicious code attacks is a serious threat to organizations worldwide. From phishing attacks to supply chain exploits, cybercriminals are using increasingly sophisticated methods to steal sensitive information. Knowing what is malicious code and understanding the types of malicious code is key to defending your infrastructure.
Every second counts in the fight against it. Protect your systems now with Xygeni’s cutting-edge malware detection tool. Contact us today or get a Free Demo and stay ahead of cyber threats!